1-3 The Japanese education system
In Japan, children begin attending school at six years old, and compulsory education lasts for a total of nine years (six years of elementary school and three years of junior high school). After twelve years of education (compulsory education + three years of high school), students may proceed to higher education (university, junior college, or professional training college).

Higher education institutions
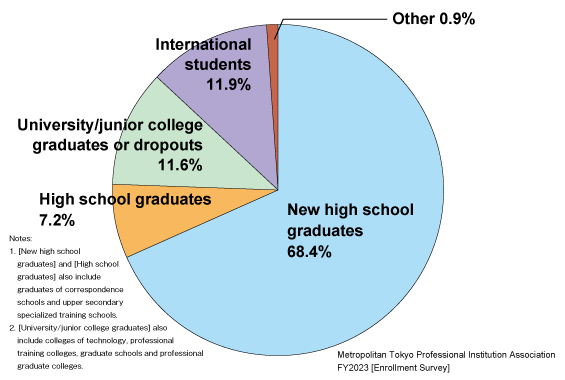
In Japan, over 70 percent of high school graduates go on to higher education institutions such as universities and professional training colleges. About 16 to 17 percent of them go to professional training colleges. The percentage of new high school graduates attending daytime courses at professional training colleges is approximately 70 percent; the rest are dropouts and graduates of universities and the like, working adults, and international students. Approximately 80 percent of international students advance to higher education after graduating from Japanese-language schools, with professional training colleges being one of the main paths.